During daydreaming, the brain’s default mode network becomes active while focus on the external environment decreases. This shift allows for creativity and problem-solving.
Daydreaming involves a complex brain activity that often goes unnoticed in our daily lives. It’s a state in which the mind wanders away from the immediate tasks, allowing for introspection and the merging of thought and memory. This not only facilitates creative thinking but also plays a role in how we consolidate memories and process emotions.
The brain does not shut down; instead, it engages different networks that contribute to our ability to generate novel ideas and solutions. Understanding the effects of daydreaming on the brain can shed light on its importance in cognitive processes and personal well-being. Engaging in daydreams can provide a valuable break for the mind, potentially boosting productivity and mental health.

Credit: www.amazon.com
The Science Of Daydreaming
Have you ever wondered what happens in your brain when you daydream? It might look like you’re doing nothing, but your brain is actually very active. Daydreaming is not just a way to escape reality. It’s a complex process that involves different brain areas. In this section, we will dive into the scientific workings behind daydreaming.
Understanding The Neural Basis Of Daydreaming
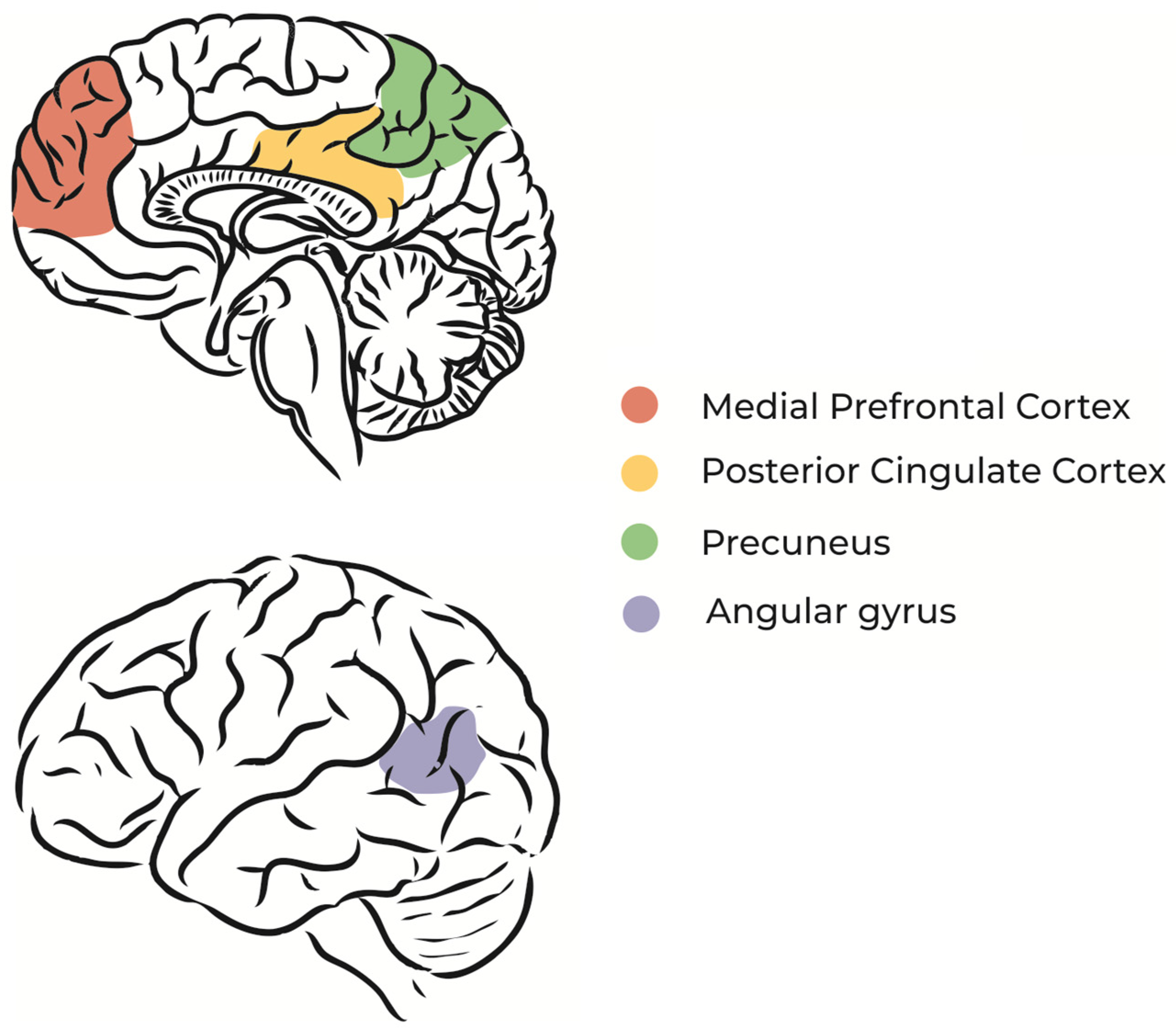
When we daydream, our brains light up. Scientists call this the brain’s default mode network (DMN). The DMN includes several brain parts. These parts work together when we are not focusing on the outside world. They help us think about our past and future. Here’s a simple breakdown of what happens:
- The medial prefrontal cortex: This part helps us think about ourselves and our goals.
- The posterior cingulate cortex: It links our memories and emotions.
- The temporoparietal junction: This area lets us consider other people’s thoughts.
Together, these areas create our daydreams. They help us solve problems and plan for the future.
Exploring The Different Types Of Daydreaming
Daydreaming comes in many forms. We can daydream about many things. Scientists often group them into two types:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive-Constructive Daydreaming | This kind is playful and wishful. It can help with creativity. |
| Guilty-Dysphoric Daydreaming | This involves worries or fears. It can sometimes be linked to mood problems. |
No matter the type, daydreaming shapes our emotions and thoughts. It helps us relax and be more creative.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Cognitive Functions And Daydreaming
Daydreaming often gets a bad rap as a waste of time. Yet, our brains are hard at work during these mental wanderings. Cognitive functions relating to memory, problem-solving, and emotional health see a boost. When we daydream, our mind explores and processes without the typical constraints of focused thinking.
Memory Consolidation And Enhancement
Daydreaming plays a key role in memory. Through periods of reflection, our brains sort and store information. This is known as memory consolidation. A daydream can serve as a bridge between learning and remembering.
- Links new information to existing knowledge.
- Strengthens neural connections for better recall.
- Creates a wider network of memories, helping us remember more.
Problem-solving And Creativity
Thinking outside the box? Daydreaming might be to thank. When the mind is free to roam, it can make creative connections. It might also solve problems in unexpected ways. It’s a silent brainstorm session without any rules.
- Encourages new perspectives on challenging tasks.
- Allows subconscious processing leading to ‘Eureka!’ moments.
- Fosters innovative ideas by blending thoughts and experiences.
Emotional Regulation And Mental Health
Daydreaming can be a stress reliever. It gives the brain a break from daily pressures, leading to better emotional health. Floating in a daydream can offer a quick escape, providing a mental reset.
Benefits include:
| Emotional Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Mood Improvement | Shifts focus from stress to calming thoughts. |
| Resilience Building | Fosters a stronger, more adaptable mindset. |
| Anxiety Reduction | Lowers immediate feelings of anxiousness. |
Practical Applications And Benefits Of Daydreaming
The Practical Applications and Benefits of Daydreaming often go unnoticed in a world that values constant hustle. Yet, slipping into a daydream can unlock several advantages, enhancing our daily lives in ways we might not expect.
Boosting Productivity And Focus
Think of daydreaming as a brief vacation for your mind. This mental escape can lead to a surge in productivity upon return. A wandering mind can hit the refresh button, making tasks seem less daunting. Studies show that daydreaming can improve focus over long periods, especially if engaged in activities that require constant attention. Enhanced focus leads to better performance, making daydreams a potential asset in your productivity toolkit.
Enhancing Mental Well-being
- Stress reduction
- Mood improvement
- Creative boosts
Daydreaming contributes to mental health by offering a much-needed break from reality. It can reduce stress, enhance mood, and spark creativity. Imagining pleasing scenarios can trigger the release of endorphins, helping not just with relaxation but also with a more positive outlook. Embrace those brief escapes to keep your spirits high and your ideas fresh.
Promoting Self-reflection And Goal-setting
Daydreams are not just flights of fancy; they are a breeding ground for self-reflection and goal-setting. Often, our wandering minds tackle unresolved questions or ambitions. They can lead to greater self-awareness and a clearer vision for future goals. Daydreams allow us to play out scenarios and pathways, helping us chart a course towards our aspirations.
| Aspect | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Self-discovery | Find inner desires and motivations |
| Goal-visualization | See and plan achievable steps |

Credit: www.cell.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of Brain Effects During Daydreaming
What Triggers Brain Daydreaming?
Daydreaming often occurs during low-engagement tasks or activities. Mundane tasks like showering or commuting can trigger this state. The brain shifts into a default network, promoting internal thought and reflection.
How Does Daydreaming Affect Focus?
During daydreaming, focus shifts from the external environment to internal thoughts. This can disrupt immediate task performance but may enhance problem-solving and creativity. Attention management becomes essential to balance productivity and the benefits of mind-wandering.
Can Daydreaming Improve Creativity?
Yes, daydreaming can foster creativity. It allows the brain to explore ideas without restrictions. This freedom can lead to novel connections and solutions. Frequent daydreamers often exhibit high levels of creativity.
Is Daydreaming Beneficial To Mental Health?
Moderate daydreaming is beneficial to mental health. It offers a mental break, reducing stress and refreshing the mind. However, excessive daydreaming may negatively impact real-life interaction and responsibilities.
Conclusion
Daydreaming isn’t just a distraction—it’s a complex brain function. This mental escape can spark creativity and relieve stress. It offers a pause in our busy lives, letting our minds wander and refresh. Remember, occasional daydreams can be beneficial. So next time your mind drifts, embrace the journey it takes you on.

