P53, also known as TP53, is a tumor suppressor protein crucial for regulating cell division and preventing cancer. It acts as a genomic guardian, ensuring cellular integrity.
Understanding P53 is imperative for grasping the complexities of cellular mechanisms in health and disease. This protein serves as a pivotal factor in cellular response to DNA damage and other stress signals by either halting cell cycle progression to allow DNA repair or by initiating apoptosis, the programmed cell death.
Its role as a tumor suppressor earns it significant attention in cancer research; mutations in the P53 gene can lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation, contributing to tumor development. P53’s ability to activate DNA repair proteins when DNA sustains damage further underlines its protective nature. Within the realm of medical research and therapeutics, the study of P53 extends to numerous applications, from understanding cancer pathways to designing targeted treatments. This makes P53 a key molecular protagonist in the quest for innovative strategies against cancer.
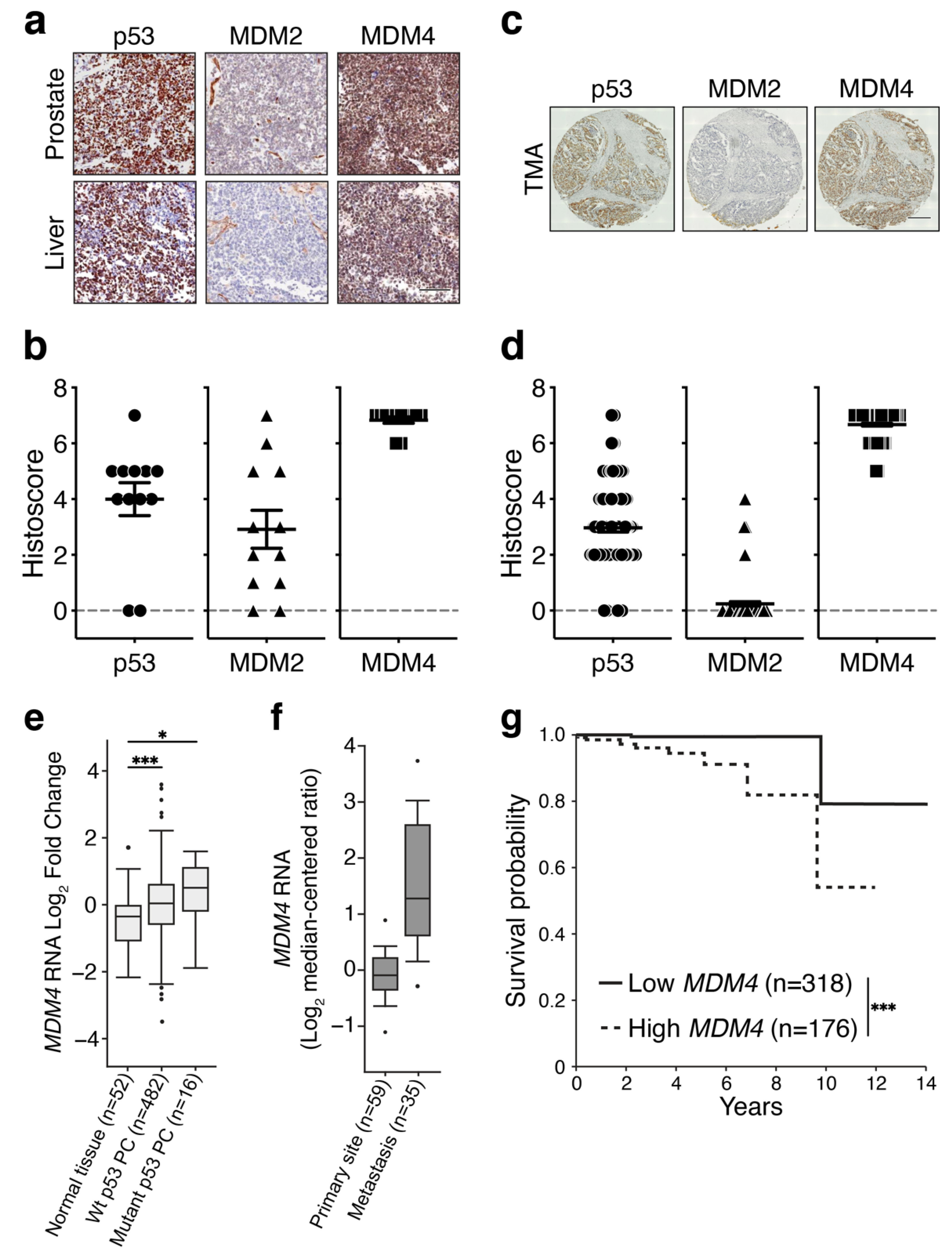
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Role Of P53 In Cancer
The p53 protein is like the body’s own superhero, protecting our cells from becoming cancerous. It watches over the cells, making sure they grow and divide as they should. When something goes wrong, p53 springs into action, halting the spread of potentially cancerous cells. Understanding its role offers insight into how cancers develop and ways to design new treatments.
Tumor Suppressor Function
The main job of p53 is to act as a tumor suppressor. This means it helps stop cells from growing too fast or in a way that’s not normal. p53 can tell a cell to slow down, fix itself, or even die if it’s too damaged. This is crucial because cells that don’t listen to these signals can turn into cancer.
Regulation Of Cell Cycle
Cell cycle regulation is another important task for p53. The cell cycle is a series of steps that cells go through to grow and divide. p53 works like a quality control inspector, checking cells at each step. If it finds a problem, p53 can stop the cell cycle, giving the cell time to repair or calling for its destruction to prevent harm.
Dna Repair Mechanism
p53 also keeps an eye on the DNA repair process. DNA can get damaged by things like the sun’s rays or chemicals in smoke. Normally, cells fix this damage. But sometimes, they need a little help. That’s where p53 comes in. It makes sure cells mend their DNA properly. If the damage is too bad, p53 tells the cell to die so the damage doesn’t spread.
Mutations In P53
The guardian of our genome, p53, plays a crucial role in preventing cells from turning cancerous. This protein acts as a quality control agent. It stops cells with damaged DNA from dividing. Without p53, cells could grow out of control. That is how tumors form. But what happens when p53 itself is not working properly? Let’s delve into the world of p53 mutations and see how they affect us.
Types Of P53 Mutations
P53 mutations can be of various types, each altering the gene in distinct ways:
- Missense mutations – One amino acid in the protein changes.
- Nonsense mutations – The mutation signals the cell to stop making the protein too soon.
- Insertions or deletions – These either add or remove a piece of DNA in the p53 gene.
- Splice-site mutations – They affect how the gene’s instructions are read to make the protein.
Impact On Protein Function
Changes in p53 can stop it from working. This can let damaged cells divide. Here’s what mutations can do to p53:
| Mutation Type | Protein Impact |
|---|---|
| Missense | Changes shape of p53 protein |
| Nonsense | Makes a short, non-working protein |
| Insertions/Deletions | Leads to a faulty protein |
| Splice-site | Interferes with protein assembly |
Association With Cancer Development
P53 mutations are linked with many cancers. This includes:
- Lung cancer
- Breast cancer
- Colorectal cancer
- Brain tumors
- Leukemia
When p53 doesn’t work right, it can’t play defense. Cells with mutations multiply. This is often how cancer starts. That’s why p53 is dubbed the “guardian of the genome.” Keeping it in shape is key to stopping tumors from forming.
Therapeutic Targeting Of P53
P53, often referred to as the “guardian of the genome,” holds a key role in preventing cancer. Its function in the regulation of cell division and its ability to initiate the repair of damaged DNA make it a prime target for cancer therapy. Advances in medical science have opened the door to targeted treatments aimed at P53. This could restore normal function to cells or eliminate those with harmful mutations. Let’s delve into the potential of P53 as a therapeutic target.
Restoring Wild-type P53 Function
The loss of normal P53 function can contribute to uncontrolled cell growth, a hallmark of cancer. Restoring this function has gained much attention. Specific molecules designed to reactivate wild-type P53 can potentially halt the progression of cancer.
- Gene therapy techniques introduce functional P53 into cells.
- Small molecules can revive damaged P53, forcing cancer cells to self-destruct.
Targeting Mutant P53 For Degradation
Mutations often render P53 ineffective. Strategies to target these mutant forms of P53 aim to remove these detrimental proteins. This removal can revive the cell’s natural ability to fight cancer.
- PROTACs (Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras) tag mutant P53 for destruction.
- Drug development focuses on compounds that stimulate the breakdown of abnormal P53.
Emerging Therapies
Cutting-edge therapies are continually being developed to combat cancer through manipulation of P53. These therapies offer a glimmer of hope in the war against various forms of cancer.
Examples include:
| Therapy Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Immunotherapy | Leveraging the immune system to recognize and target P53-related abnormalities. |
| Peptide Therapy | Using peptides that mimic P53 functionality to suppress tumor growth. |
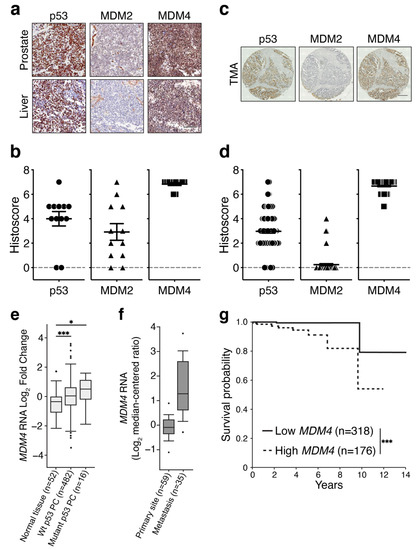
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Credit: scitechdaily.com
Frequently Asked Questions On P53
What Is The P53 Gene?
P53, often referred to as the “guardian of the genome,” is a crucial protein in regulating cell division and preventing cancerous growth. By repairing DNA or initiating cell death, it ensures damaged cells don’t multiply.
How Does P53 Fight Cancer?
P53 fights cancer by acting as a tumor suppressor. It halts cell division when DNA damage is detected and can trigger apoptosis (cell suicide) if the damage is beyond repair. This prevents the proliferation of potentially cancerous cells.
What Causes P53 To Malfunction?
Mutations in the P53 gene itself can cause it to malfunction. Such mutations are common in human cancers. These changes in P53’s structure impede its ability to regulate cell growth and DNA repair.
Can P53 Mutations Be Inherited?
Yes, P53 mutations can be inherited, particularly in a rare disorder called Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Individuals with this condition have a higher risk of developing various cancers at an early age due to inherited P53 mutations.
Conclusion
Understanding p53’s pivotal role in cellular function is crucial. This protein acts as a guardian against cancer, ensuring DNA integrity and cell cycle regulation. Embracing the importance of p53 may lead to groundbreaking advances in cancer research. Let’s continue to explore p53’s potential for fostering revolutionary treatments and therapies.