Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition triggered by a terrifying event. Those affected may experience flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety.
Understanding Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder is crucial for recognizing the impact of traumatic events on individuals’ mental health. PTSD can result from various experiences, such as military combat, natural disasters, serious accidents, or personal assaults. Symptoms often include persistent and disturbing thoughts related to the trauma, emotional numbness, and an increased fight-or-flight response, which may significantly disrupt a person’s daily life.
While the disorder is most associated with veterans, it can affect anyone who has undergone a traumatic experience. Early detection and treatment are vital in managing PTSD effectively, which may include therapy, medication, or a combination of both. Support from family, friends, and support groups can also play a key role in recovery, helping those affected to regain control over their lives.
What Is Post-traumatic Stress Disorder?
Imagine your mind stuck on a terrifying event, reliving it over and over. This is a glimpse into Post-traumatic Stress Disorder, or PTSD, a mental health condition triggered by seeing or experiencing a traumatic event. It’s like a shadow clinging to the memories, refusing to let go.
Definition
PTSD is a severe psychological reaction following a period of extreme stress or a disturbing event. It’s not just about feeling upset; it’s a condition that can change how a person thinks, feels, and behaves.
Causes
PTSD doesn’t just appear without reason. Its seeds are often sown in moments of profound stress. Here are common causes:
- Military combat exposes soldiers to dangerous situations.
- Violent assaults, like robbery or mugging, shake a person’s sense of safety.
- Natural disasters, such as earthquakes or hurricanes, bring chaos and loss.
- Severe accidents or injuries can create lasting mental scars.
- Abuse or neglect during childhood leaves deep emotional wounds.
Symptoms
PTSD can show itself in many ways, making life hard for those who suffer. Symptoms usually begin early, typically within 3 months of the incident, but sometimes they emerge years afterward. Major symptoms include:
| Type | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Intrusion | Flashbacks, nightmares, and unwanted memories. |
| Avoidance | Staying away from reminders of the trauma. |
| Alterations in cognition and mood | Memory issues, negative thoughts, and emotional numbness. |
| Changes in arousal and reactivity | Being easily startled, feeling tense, and having difficulty sleeping. |

Credit: www.sabinorecovery.com
Diagnosis And Treatment
Understanding Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) starts with recognizing its symptoms and seeking help. Diagnosis comes before treatment. Doctors use certain criteria to diagnose. Many therapies and medications exist for PTSD treatment.
Diagnostic Criteria
Doctors follow the DSM-5 manual to diagnose PTSD. Patients must have exposure to a traumatic event. Following this, patients experience symptoms that can include flashbacks, avoidance, and mood changes. Symptoms must last for more than a month for a clear diagnosis. Detailed interviews and assessments help doctors understand the patient’s condition.
Therapy Options
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Improves coping skills. CBT aims to change negative thought patterns.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): Helps process trauma. Patients recall events while focusing on a moving object.
- Prolonged Exposure Therapy: Teaches patients to face their fears. Patients are exposed gradually to trauma-related cues and memories.
- Group Therapy: Provides a support network. Patients share experiences in a group setting.
Medications
Doctors often prescribe medicines to help with PTSD symptoms. These can reduce anxiety, improve sleep, and stabilize mood. Common medications include:
| Type | Medication Example |
|---|---|
| SSRIs | Sertraline, Paroxetine |
| SNRIs | Venlafaxine |
| Prazosin | Minipress |
Choosing the right medication depends on individual symptoms and health history. Regular follow-ups with the doctor ensure medications are effective and safe.
Risk Factors
Understanding the risk factors for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is key. PTSD does not discriminate. It can happen to anyone. Let’s explore what increases the chance of experiencing this mental health condition.
Exposure To Trauma
Directly facing a traumatic event is a major risk factor for PTSD. This might include:
- Combat exposure for military personnel
- Physical or sexual assault victims
- Survivors of serious accidents or natural disasters
Repeated exposure to harrowing details of trauma can also lead to PTSD.
Personal Vulnerability
Genetic makeup and personality traits might make some people more susceptible to PTSD:
| Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Genetics | A history of mental illness in the family may increase risk |
| Temperament | High stress or anxiety levels can impact how one handles trauma |
| Previous Trauma | Earlier traumatic experiences amplify vulnerability |
Lack Of Social Support
After a traumatic event, having a strong support system is crucial. Lack of such support can increase PTSD risk. Key points include:
- Emotional backup from friends and family helps in coping
- Access to community resources provides a safety net
- Feeling isolated can worsen PTSD symptoms dramatically
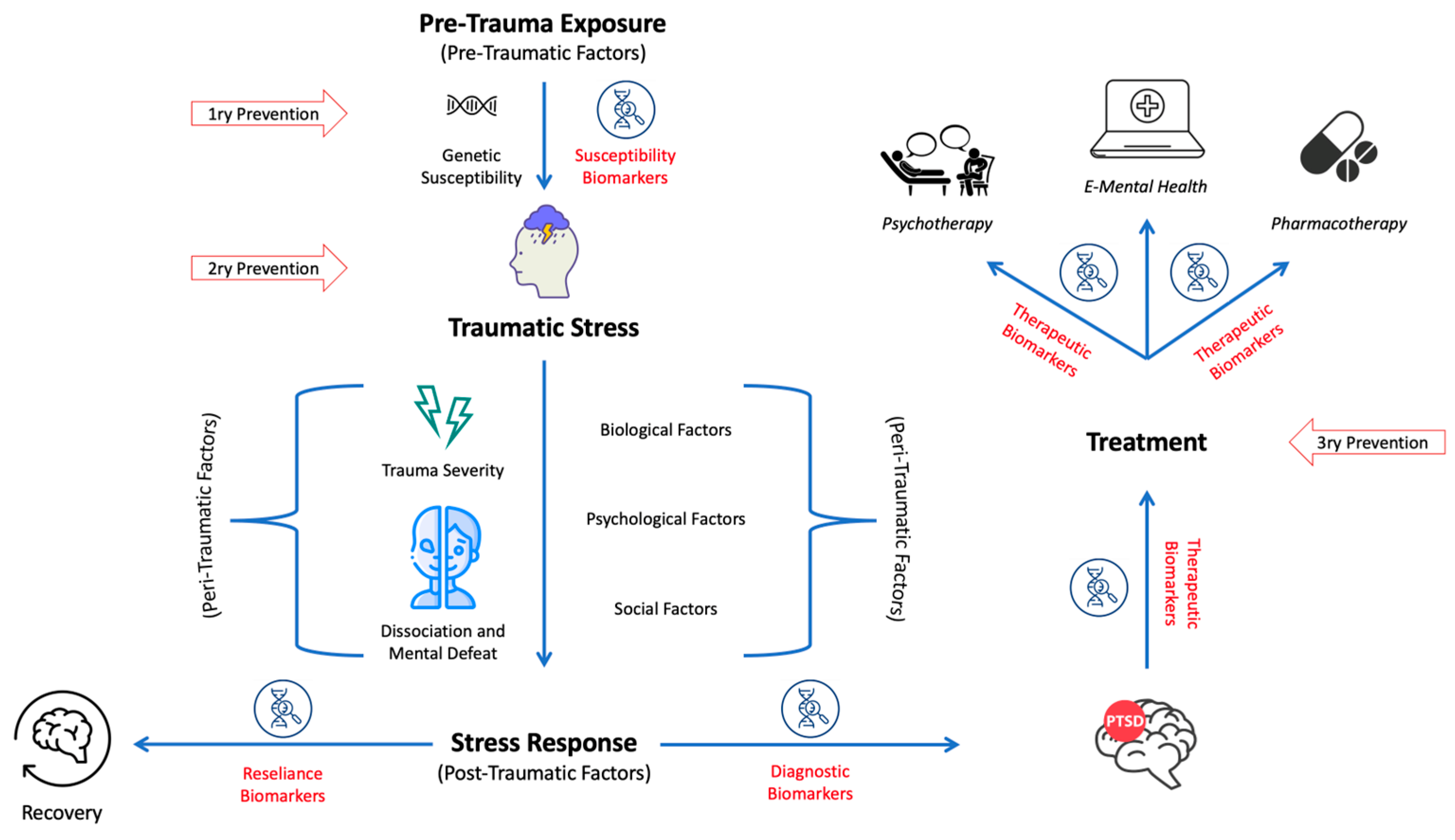
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Effects Of Ptsd
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) touches lives profoundly. It’s a condition that follows after experiencing or witnessing severe trauma. The effects of PTSD ripple through emotions, physical health, and relationships. Let’s explore how this disorder impacts these areas.
Emotional Impact
PTSD exerts a heavy emotional toll. Individuals may relive the traumatic event through flashbacks. Nightmares can disrupt sleep. During the day, sudden memories can cause intense distress. People may feel guilt or depression. In severe cases, they may feel disconnected from reality, a condition known as dissociation.
- Flashbacks and memories that intrude daily life
- Nightmares that disrupt sleep
- Intense distress with sudden recollection of the trauma
- Guilt or depression that persists
- Dissociation, a feeling of detachment from reality
Physical Health Consequences
The stress from PTSD can harm the body. This stress can lead to headaches and dizziness. Muscle tension might be a continuous battle. Exhaustion can be commonplace. Symptoms such as these can increase the risk of heart disease. Immune system function might suffer, leading to more colds and infections.
- Headaches and dizziness that affect day-to-day activities
- Muscle tension that creates constant discomfort
- Exhaustion that impairs overall wellbeing
- Risk of heart disease due to ongoing stress
- Weakened immune system leading to more frequent illness
Relationship Challenges
Relationships often bear the brunt of PTSD. Trust issues can arise. Intimacy may become difficult. Many feel irritable, leading to conflicts. Withdrawal from social activities is common. These challenges can strain personal and professional relationships.
- Trust issues that strain connections
- Difficulty with intimacy affecting close relationships
- Irritability that can lead to arguments
- Social withdrawal resulting in isolation
- Strained personal and professional relationships impacting overall quality of life
Prevention And Coping Strategies
Understanding Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is vital in addressing its impacts. This section dives into effective strategies for preventing and coping with PTSD, focusing specifically on Education and Awareness, Building Resilience, and Seeking Support. These strategies help individuals at risk of or struggling with PTSD to manage symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Education And Awareness
Knowledge is power when confronting PTSD. Education and awareness play a crucial role in both preventing PTSD and coping with it after trauma. Being informed about the causes, symptoms, and treatments can significantly reduce the stigma associated with the disorder, leading to better outcomes for those affected.
- Learn the common triggers and stress responses.
- Understand the importance of early intervention.
- Know where to find resources and assistance.
Building Resilience
Resilience is a shield against stress-induced health conditions, including PTSD. By developing resilience, individuals can bounce back from adversity more effectively.
| Technique | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Mindfulness | Reduces anxiety and stress |
| Healthy lifestyle choices | Improves overall well-being |
| Positive thinking | Encourages a hopeful outlook |
Seeking Support
Never underestimate the value of a strong support system. Engaging with family, friends, or support groups can provide comfort and practical assistance. For those coping with PTSD, establishing a network of support is a cornerstone of recovery.
- Reach out to loved ones for emotional support.
- Connect with PTSD support groups to share experiences.
- Consult healthcare professionals for expert guidance.

Credit: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Frequently Asked Questions On Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
What Triggers Post-traumatic Stress Disorder?
PTSD is triggered by experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. This includes natural disasters, war, serious accidents, or personal assaults. Not everyone exposed to such events develops PTSD; individual coping mechanisms and emotional support play a role.
How Is Ptsd Diagnosed?
PTSD is diagnosed through clinical evaluation by a mental health professional. They use the DSM-5 criteria, which include assessing exposure to traumatic events, intrusive memories, avoidance behaviors, mood changes, and increased reactivity symptoms.
Can Ptsd Be Cured?
While PTSD cannot always be completely cured, it can be effectively managed. Treatment often includes therapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), medications like SSRIs, and self-care strategies. Early intervention can improve long-term outcomes.
What Are The Signs Of Ptsd?
Common signs of PTSD include flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts about the traumatic event. Sufferers may also avoid places or people that remind them of the trauma, and experience emotional numbness or irritability.
Conclusion
Navigating the journey toward healing from PTSD is a personal process. Support, understanding, and the right tools can make a significant difference. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength. With time, patience, and effort, resilient strides can lead to overcoming life’s traumas.
Embrace each step forward.

