Sodium-ion batteries offer a low-cost alternative to lithium-ion batteries. They operate using sodium ions, which are more abundant than lithium.
Exploring the world of rechargeable batteries, two prominent types stand out: sodium-ion and lithium-ion. Cost-effectiveness and sustainability are the driving factors behind the rising interest in sodium-ion batteries, as they tap into the abundant supply of sodium compared to the rarer lithium resources.
Lithium-ion batteries, on the other hand, boast a higher energy density and a longer track record in applications from smartphones to electric vehicles. Both technologies share a similar working principle, where ions move between electrodes through an electrolyte, yet they inherently differ in electrochemical performance, lifecycle, and environmental footprint. As the demand for energy storage solutions continues to soar, the competition between these two battery types is intensifying, prompting indispensable innovations for a future powered by renewable energy.

Credit: www.ft.com
Comparing Sodium-ion And Lithium-ion Batteries
The quest for efficient, cost-effective energy storage brings us to a comparison of sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries. Both technologies are pivotal in powering a range of devices, from mobile phones to electric vehicles. Understanding their differences helps in making informed decisions for various applications.
Energy Storage Capacity
The storage capacity of a battery indicates how much energy it can hold. Lithium-ion batteries generally have a higher energy density. This means they store more energy for their size.
On the other hand, sodium-ion batteries typically have a lower energy density. But, they show potential for improvements with ongoing research.
Charging And Discharging Performance
How fast a battery can charge and discharge is crucial for its performance. Lithium-ion batteries charge quickly and offer high discharge rates. They are reliable for power-hungry devices.
In contrast, sodium-ion batteries are catching up. They offer respectable charging speeds. But, their discharge rates are generally slower compared to lithium-ion.
Cost And Availability
The abundance of materials affects the cost and availability of batteries. Sodium is more abundant than lithium. This makes sodium-ion batteries potentially cheaper and more accessible.
| Aspect | Lithium-ion | Sodium-ion |
|---|---|---|
| Abundance | Less Abundant | More Abundant |
| Cost | Higher Cost | Lower Cost |
| Accessibility | Less Accessible | More Accessible |
Lithium-ion batteries, while more efficient, face cost fluctuations. This is due to limited lithium reserves.
Advantages Of Sodium-ion Batteries
The shift towards sustainable energy storage is accelerating. Sodium-ion batteries are emerging as a potent alternative to their lithium-ion counterparts. They offer distinct advantages that promise a more sustainable and economically viable future in energy storage.
Lower Cost
Sodium-ion batteries are more cost-effective than lithium-ion batteries. The reasons are simple:
- Sodium is cheaper to source, reflecting directly on the manufacturing costs.
- Less complex manufacturing processes contribute to lower production expenses.
- The cost of the active material in sodium-ion batteries is significantly lower.
Abundance Of Sodium
Sodium is far more plentiful than lithium, making sodium-ion batteries a sustainable choice.
Here are a few points that stand out:
- Sodium is the sixth most abundant element on Earth.
- It is readily available in seawater and crustal rocks.
- This abundance ensures a steady and reliable supply chain.
Advantages Of Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are popular. They power many devices. Let’s learn why they are good.
Higher Energy Density
Lithium-ion batteries hold more power. This means devices last longer on a single charge. The batteries are small but strong. They are great for phones and laptops.
Better Cycle Life
These batteries can be charged many times. They don’t wear out fast. This makes them reliable for daily use.
Energy Density Table
| Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) |
|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | 150-200 |
| Sodium-ion | 90-120 |
Cycle Life Points
- Long-lasting performance – keeps your device running over time.
- More recharge cycles – compared to other battery types.
- Sustainable power – for frequent uses.

Credit: www.amazon.com
Applications And Future Outlook
Peering into the world of batteries, we notice two stars: Sodium-Ion and Lithium-Ion. Each holds unique merits and serves different gadgets. Let’s dive into their present roles and what tomorrow may hold for these energy champions.
Current Applications
Lithium-Ion batteries light up our lives in phones, laptops, and electric cars. Their high energy density makes them ideal for tech that needs to stay powered on the go.
Sodium-Ion batteries are newer players in the market. They are finding their space in less energy-intensive applications. Think about storage for renewable energy and electric bikes.
Potential Future Developments
Research aims to boost Sodium-Ion batteries for broader use. Here’s what’s sparking excitement:
- Better energy capacity could rival Lithium-Ion.
- Lower costs make them attractive for large-scale storage.
- Eco-friendly materials are a win for our planet.
Will Sodium-Ion overtake Lithium-Ion? Time will tell, but the race is on to power our future in smarter ways.
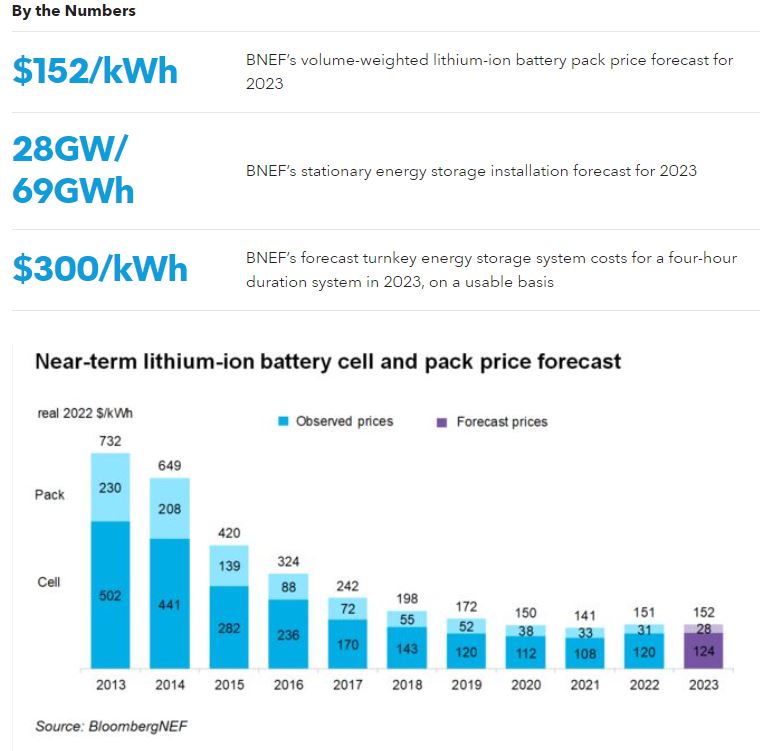
Credit: about.bnef.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Sodium-ion Battery Vs Lithium-ion Battery With Diagram
What Is A Sodium-ion Battery?
A sodium-ion battery utilizes sodium ions as charge carriers. It’s an alternative to lithium-ion batteries, offering cost-effectiveness due to sodium’s abundance. They are suited for grid storage solutions.
How Does Lithium-ion Battery Work?
Lithium-ion batteries function by transferring lithium ions between anode and cathode through an electrolyte. They are known for their high energy density and are widely used in portable electronics.
What Are The Advantages Of Sodium-ion Batteries?
Sodium-ion batteries are less expensive than lithium-ion, due to the abundance of sodium. They are safer and have a lower environmental impact, making them attractive for large-scale storage.
Can Sodium-ion Replace Lithium-ion Batteries?
Sodium-ion batteries hold potential for replacing lithium-ion in some applications, especially where cost, availability, and thermal stability are primary concerns.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries is crucial for smart energy choices. Our comparison, complete with diagrams, clearly demonstrates each battery’s strengths and potential applications. To select the best power source for your needs, consider the insights shared.
Embrace innovation, and stay tuned for future advancements in battery technology.

